Seismic Acquisition: The Basic Idea
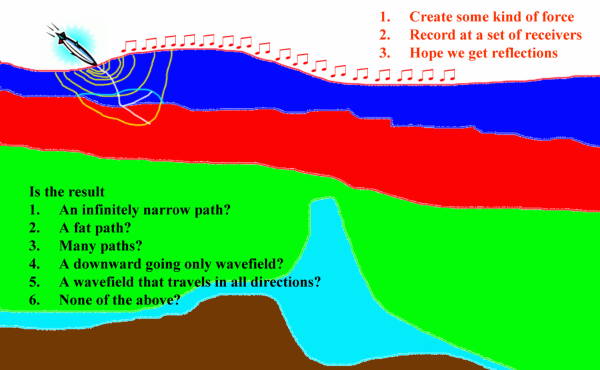
The basic idea underlying seismic acquisition is shown in Figure 1. The application of a sound source at a fixed point on the surface of the Earth produces a down-going wavefield. As the wavefield propagates, it is, hopefully, reflected as an up-going wavefield that is recorded on a series of receivers located near the surface. The job of modeling is to simulate this thought experiment as accurately as possible. From a physical point of view the model is viewed as a collection of particles that move (compress and expand or shear) under the influence of the sound source. As we can easily infer from Figure 1 such compression and rarefaction can be quite complex and occur in any direction at any given time instant.
As we progress through this book, we will see that there are many approaches to synthesizing seismic data in both simple and complex Earth models. Each approach is based on a unique approximation to a governing wave equation. Each approximation has its own unique set of limitations that compromises the accuracy of the final synthetic. In the past, these approximations were a necessary evil fostered by the computational limits of the era. The list of questions posed in Figure 1 hint at some of the limitations of the various approximations. Ranging from algorithms based on rays (infinitely narrow paths), to wavefields that travel in only one direction, and then to wavefields traveling in all directions, these limitations can have a serious impact on the quality of both the modeling and the migration algorithm under consideration. As computers become more and more efficient, these compromises will fall by the wayside and be fully replaced by the most accurate method available for the given data.
- Introduction
- Seismic Modeling
- Primary Concerns
- Three Earth Models
- Seismic Acquisition: The Basic Idea
- Why Model?
- Waves and Wavefields
- The Scalar Wave Equations
- Stress-Strain Equations
- Algorithms
- Variational Formulation and Finite Elements
- Finite Differences
- Model Boundaries
- Fourier Based Methods
- A Word About Sources
- Huygens Principle and Integral Methods
- Raytracing
- Raytrace Modeling
- Zero Offset Modeling
- History
- Zero Offset Migration Algorithms
- Exploding Reflector Examples
- Prestack Migration
- Prestack Migration Examples
- Data Acquisition
- Migration Summary
- Isotropic Velocity Analysis
- Anisotropic Velocity Analysis
- Case Studies
- Course Summary